How to Upload Wspr Spots From Wsjt
| Programmer(due south) | Joe Taylor, K1JT |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2008 |
| Written in | Python (GUI), Fortran, C [one] |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Available in | English, Italian, Spanish, French, German, Japanese, Polish, Portuguese, Russian |
| Blazon | Amateur radio and DSP |
| License | GPL |
| Website | physics.princeton.edu/pulsar/K1JT/wspr.html |
WSPR (pronounced "whisper") stands for "Weak Signal Propagation Reporter". Information technology is a protocol, implemented in a computer programme, used for weak-signal radio communication between amateur radio operators. The protocol was designed, and a program written initially, by Joe Taylor, K1JT. The software code is at present open source and is developed past a small squad. The program is designed for sending and receiving low-power transmissions to examination propagation paths on the MF and HF bands.
WSPR implements a protocol designed for probing potential propagation paths with depression-ability transmissions. Transmissions carry a station's callsign, Maidenhead grid locator, and transmitter power in dBm. The plan can decode signals with a signal-to-dissonance ratio as low as −28 dB in a 2500 Hz bandwidth.[2] Stations with net access tin can automatically upload their reception reports to a central database chosen WSPRnet, which includes a mapping facility.
The WSPR Protocol [edit]
The type of radio emission is "F1D", frequency-shift keying. A message contains a station'due south callsign, Maidenhead grid locator, and transmitter ability in dBm.[3] The WSPR protocol compresses the data in the message into 50 bits (binary digits). These are encoded using a convolutional code with constraint length 1000 = 32 and a rate of r = 1⁄2 .[three] [4] The long constraint length makes undetected decoding errors less probable, at the cost that the highly efficient Viterbi algorithm must be replaced by a simple sequential algorithm for the decoding procedure.[3]
Protocol specification [edit]
The standard message is <callsign> + <four graphic symbol locator> + <dBm transmit ability>; for example "K1ABC FN20 37" is a indicate from station K1ABC in Maidenhead grid jail cell "FN20", sending x3.7milliwatts, or near 5.0 Watts (legal limit for 630 one thousand). Letters with a compound callsign and/or 6 digit locator use a two-transmission sequence. The first transmission carries chemical compound callsign and power level, or standard callsign, 4 digit locator, and power level; the second transmission carries a hashed callsign, six digit locator, and power level. Add together-on prefixes can be up to three alphanumeric characters; add-on suffixes can be a single letter or one or ii digits.
- Standard message components after lossless compression:
- 28 bits for callsign,
- 15 bits for locator,
- 7 bits for ability level,
- full: 50 bits.
- Forward error correction (FEC):
- non-recursive convolutional code with constraint length K = 32, rate r = 1⁄2 .
- Number of binary channel symbols:
- nsym = (l + K − 1) × ii = 162.[3]
- Keying rate is 12000⁄8192 = 1.4648 baud.
- Modulation is continuous phase 4 FSK, with 1.4648 Hz tone separation.

This is a picture of an Agilent Modulation Domain Analyzer 53310A showing the narrow ring iv-FSK signal. The signal is produced by a Raspberry Pi reckoner.
- Occupied bandwidth is almost 6 Hz
- Synchronization is via a 162 bit pseudo-random sync vector.
- Each channel symbol conveys one sync bit (LSB) and 1 data bit (MSB).
- Elapsing of manual is 162 × 8192⁄12000 = 110.6 southward.
- Transmissions nominally offset one second into an even UTC infinitesimal: e.thousand., at hh:00:01, hh:02:01, etc.
- Minimum Due south/North for reception is around –34 dB on the WSJT scale (2500 Hz reference bandwidth).
Applications [edit]

Raspberry Pi as WSPR transmitter
The protocol was designed to test propagation paths on the LF, MF and HF bands. Also used experimentally at VHF and higher frequencies.
Other applications include antenna testing, frequency stability and frequency accurateness checking.
Usually a WSPR station contains a reckoner and a transceiver, but it is too possible to build very elementary beacon transmitters with little endeavour.
For case a simple WSPR beacon can exist built using the Si 570,[v] or Si 5351.[6] The Raspberry Pi can also be used as WSPR beacon.
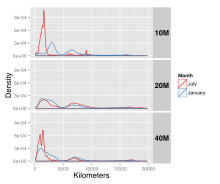
Density distribution of WSPR spots, January 2014 vs July 2014, using only virtually afar reception per spot.
An accurate clock is essential both for manual and decoding of received signals.
MH370 [edit]
In May 2021, aerospace engineer Richard Godfrey suggested an examination of historical WSPR data to further define the flying path of Malaysian Airlines flight MH370 on 8 March 2014, suggesting that there were "518 unique manual paths that cross the surface area of interest effectually Malaysia, the Malacca Strait and the Indian Ocean. With the WSPR data provided every ii minutes and the ability to check against the satellite data every 60 minutes it is possible to find and track MH370 from two independent sources."[seven] In November 2021, Godfrey reported that analysis using WSPR technology indicated the aircraft flew in circles for around 22 minutes in an area 150 nautical miles from the coast of Sumatra earlier vanishing.[eight] Later that month, Godfrey announced a proposed search area with a radius of twoscore.0 nautical miles (74.1 km) centered effectually 33°10′37″Southward 95°18′00″Eastward / 33.177°Southward 95.3°E / -33.177; 95.3 in the southern Indian Ocean. This new location was identified through extensive analysis of carve up data sets, including Inmarsat satellite data, Boeing performance data, oceanographic floating debris drift data, and WSPR net data.[ix] [10]
In February 2022, the Australian Send Rubber Agency and Geoscience Australia confirmed they have renewed the search for MH370 past reviewing former data, following the release of a detailed written report by Godfrey.[eleven] Marine robotics visitor Ocean Infinity aims to resume the search for MH370 in the commencement half of 2023.[12]
History [edit]
WSPR was originally released in 2008.
References [edit]
- ^ "WSJT Programme Development Page". physics.princeton.edu.
- ^ "WSJT Dwelling Page". physics.princeton.edu.
- ^ a b c d Joe Taylor, K1JT: WSPRing Around the Globe. QST November (2010), p. thirty-32.
- ^ G4JNT: The WSPR Coding Process: Non-normative specification of WSPR protocol
- ^ WSPR Beacon with Si 570 and Atmel AVR http://wsprnet.org/drupal/sites/wsprnet.org/files/si570wspr.pdf
- ^ QRSS/WSPR Transmitter Kit https://qrp-labs.com/
- ^ Malaysia Airlines flight MH370 left 'fake trails' before disappearing, new inquiry suggests, Anne Barker, ABC News Online, 2021-05-05
- ^ "Engineer says doomed MH370 airplane 'flew in circles for 20 mins earlier vanishing'". New York Post. Nov 10, 2021.
- ^ Browning, Simon (3 December 2021). "MH370: Could missing Malaysian Airlines airplane finally be found?". BBC . Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "GDTAAA WSPRnet MH370 Analysis Flying Path Study.pdf" (PDF). Dropbox . Retrieved half dozen March 2022.
- ^ Ransley, Ellen (16 February 2022). "New technology could concord key to MH370 disappearance". News.com.au . Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Richards, Isabella (eight March 2022). "Search for MH370 to Resume in 2023". Australian Aviation . Retrieved 8 March 2022.
External links [edit]
- Official website

- Fundamental database of reception reports
- WSPRLite
- WSPR-Beacon-24DX RUS
- Live WSPR propagation analysis
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WSPR_(amateur_radio_software)
0 Response to "How to Upload Wspr Spots From Wsjt"
Post a Comment